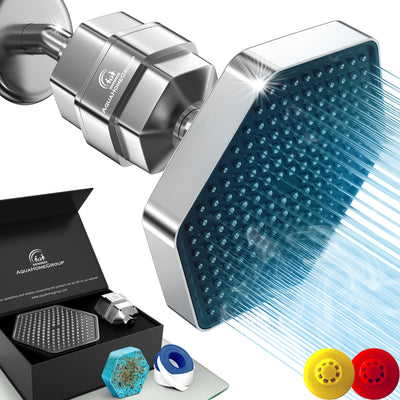
Shower water filter that remove fluoride. Filter out fluoride (Houston)
Water filter that remove fluoride
Water filters that remove fluoride are a necessary and useful remedy for people who care about their health. Let's try to understand how fluoride enters the water, how it is useful and what harm it can do to the human body.
Fluoride in water

Fluorides are one of the characteristic admixtures of ground and underground water. It is a very important component; at low concentrations it can prevent caries, and at high concentrations it accumulates in the body and causes bone disease, which is called fluorosis.
Fluorine as a chemical element belongs to the group of halogens, i.e. it stands in line with Chlorine, Brome and Iodine.
In the form of a pure substance is a gas of pale yellow color, which can be observed only in the laboratory conditions, because fluorine is the most active non-metallic element and interacts with virtually all substances, and mainly with a strong release of heat accompanied by an explosion.
This explains the fact that in environmental objects it is contained in the form of salts - fluorides.
Where does fluoride come from in water?
Fluorine compounds are found in all natural water sources.
For example, sea waters contain on average 1 mg/l, river waters - less than 0.5 mg/l, the highest concentrations in the groundwater - up to 30 mg/l (here the fluorine concentration will be determined by the rocks that make up the aquifers).
Fluorides are contained in a wide range of minerals, including melting feldspar, rock phosphates, cryolite, apatite, mica, etc. The fluoride concentration will be determined here. CaF2 is one of the minerals with low solubility limited to 40 mg/l.
Fluorides are contained in both sedimentary and magmatic rocks. In practice, their increase is typical for places:
- seaweed deposition in the foothills of mountains;
- volcanic activity;
- widespread granite and gneissic rocks.
According to recommendations of the World Health Organization fluorine rate in drinking water is 0.8 - 1 mg/dm3.
In some countries, fluorine is introduced into water pipes specifically to protect against caries. The United States was the first country to introduce fluoride into water specifically to prevent children's tooth disease.
Today, water fluorination occurs in a number of countries: the USA, Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Hong Kong, Ireland, Israel, Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Serbia, Singapore, Spain, Great Britain and Vietnam.
Also in the world about 40 million people use natural fluorinated water daily.
If the amount of fluoride in water is increased, its removal is required.
Who to water filter out fluoride and chlorine in Houston?

We have already written above that depending on its content fluorides can be both harmful and useful.
Does it need to water filter out fluoride and chlorine in Houston or any other city? There is no definite answer to this question. For a start, we must weigh the pros and cons.
Water with excess fluoride leads to a disease called fluorosis. Its mechanism is that excess fluoride displaces calcium from bone and teeth.
Primary manifestations of dental fluorosis are accompanied by pigmentation and erosion of dental tissue, after six years of age, children are less likely to have tooth fluorosis.
The next stage after tooth affection is skeleton affection. Fluoride accumulates in bone tissue for a long time. The primary signs are restricted mobility and scrap in the joints. In case of severe lesions there are changes in bone structure, ligament calcification, which cause muscle damage and pain.
As for acute effects, a single dose of 20 mg may cause nausea or vomiting, and a dose above 40 mg per kilogram of human weight may be fatal. And this is despite the fact that only 50% of people feel the taste difference of water at a concentration of 100 mg/l.
As for the prevention of caries, a concentration of 1 mg / l shows high efficiency, and at the same time has absolutely no effect on the bone structure, although it can cause slight pigmentation of teeth, which is proved by many years of research in countries that practice water fluoridation.
Principle of fluorine action on teeth

The cause of dental caries is the reproduction of bacteria in plaque, in particular Streptococcus mutants and Lactobacillus. In the process of life they absorb carbohydrates and produce organic acids. Particularly active life activity occurs with high consumption of sugars.
Fluoride has a major effect, breaking the mechanism of demineralization of caries. When pH decreases below 5.5, the acids dissolve hydroxyapatite, which is the basic component of tooth enamel. This process is demineralization. When a person does not consume sugar, the restoration or remineralization of tooth enamel occurs. A tooth defect occurs when the rate of remineralization is lower than the rate of demineralization.
Fluorides are able to form fluorapatite, which is more resistant to acidic environment and thus protect the tooth from damage while remineralization takes place.
Fluorine and Caries
Tooth fluorosis vs Caries
|
|
Caries |
Fluorosis |
|
Up to 0.3 mg/l |
200 - 300% |
3% |
|
0.3 - 0.7 mg/l |
20 - 200 % |
5-7% |
|
0.7 - 1 mg/l |
Relatively low morbidity rate |
7 - 10% |
|
1.0 - 1.5 mg/l |
Relatively low morbidity rate
|
1 level - 7-10% 2 level - 3% |
|
1.5 - 2.0 mg/l |
Relatively low morbidity rate |
1 and 2 levels- 30-40% 3 level - 3% |
Effects of fluoride on skeleton. Portable shower water filter that removes fluoride.

Fluoride content in water of 1-2 mg/l decreases ossification in children and osteoporosis in elderly people. But already with the regular use of water containing 2.5 - 6.0 mg/l of fluorides the initial degree of osteoclerosis in individuals is detected, and with a concentration of 8 mg/l there is a marked osteoclerosis in mild form in 10-15% of the population, as well as the development of severe form within 20-30 years. At 10-20 mg/l, severe osteosclerosis occurs 10-15 years later, and in children with delayed growth. At regular consumption of water containing more than 20 mg/l fluoride, severe fluorosis will be observed in 10-15 years.
At the highest concentration, acute fluorosis will be induced in 10-15 years.
To reduce fluoride concentrations in water while showering or bathing, use Portable shower water filter that removes fluoride.
As you can see, the optimal fluorine content in water has already been determined. And excess of its MPC incomparably brings more negative consequences than the lack.
Shower water filter to filter metals chlorine and fluoride

Fluoride enters the human body not only by direct use of water, but also by breathing and through the skin. When you take a hot bath or shower, a large amount of steam is formed, which contains fluorine ions, chlorine and other substances.
If the water in your home contains harmful impurities, you can reduce their penetration into your body by using water filters.
You can use a reverse osmosis system for complex water treatment. This method of purification is the best, but very expensive.
For drinking water filtration, you can use a well filter or a stationary filter that is installed under the sink.
For the purification of fluorine and chlorine water in the bathroom, shower heads and tap filters can be used shower water filter , shower heads to filter metals chlorine and fluoride.
Fluoride in water sources
Fluorine is a common element on our planet. However, it is not commonly found in the free state. Fluorine is the most electronegative and reactive: it reacts with all substances at all temperatures. In the natural environment, it is often found in combination with calcium or aluminum. For industrial purposes, fluorspar, which contains almost 50% fluorine, is used. It is mainly mined in Russia, the United States, Kazakhstan, and Mexico.
In natural water sources, the content of fluoride is due to its ability to dissolve easily. Concentrations can be as high as 100 mg/l.
The fluoride content in water from underground sources is due to:
- soil and its consistency;
- geological, physical, and chemical indicators of the area;
- rock porosity;
- temperature;
- acidity;
- depth, etc.
Indian, Kenyan, and South American waters contain more than 25 mg/L of fluoride. Almost all Russian groundwaters have more than 1.5 mg/L, and most European waters have less than 0.5 mg/L. Surface waters have lower concentrations - up to 0,3 mg/l. Azerbaijani and Kazakh water bodies are an exception - up to 11 ml/g.
The amount of fluoride you receive depends on your diet, drinking water, and air quality. Different climates lead to different water intake. That's why it's important to be careful with water purification. When you use fluoride toothpaste, you can get up to 50 mcg of fluoride, or up to 2 mcg when you rinse your teeth with fluoride elixir. Various medications and fluoride-containing air can greatly increase daily fluoride intake.
Fluoridation of drinking water
Fluoridation was first used in 1945 in the United States. Today it is used in 39 countries around the world. Drinking water fluoridation is supported by many medical organizations.
Fluoridation of water is used to fluoridate municipal water supplies. For hot countries, fluoridation is recommended up to 0.7 mg/l, and for temperate climates up to 1 mg/l.
The main reasons for fluoridation are:
- fluoride content less than 0.5 mg/l;
- Increased incidence of dental caries.
Fluoridation of drinking water requires:
- centralized water supply with pumping and water purification stations;
- qualified personnel;
- a steady supply of fluoride-containing raw materials;
- financial resources.
The pros of water fluoridation:
- reaches a large number of people regardless of their wishes;
- accessible to the poorer segments of the population;
- reduction of periodontal disease;
- low cost;
- reduction in the cost of dental staff.
Minuses are:
- centralized water supply is mandatory;
- economically irrational in small communities;
- provision of safe working conditions for the staff;
- lack of choice for the person;
- close monitoring of equipment and personnel;
- research to determine the necessary dosage.
In rural areas or sparsely populated cities, factory-made fluoridated water is recommended. School water fluoridation programs, where a fluoride solution is added to the water tank, are also popular.
Fluoride abatement
Several methods are used to reduce fluoride levels in drinking water:
- chemical;
- physical;
- electrolytic.
In chemical water treatment, certain reagents are used. These are often aluminum and magnesium oxides. Fluoride and fluoride ions bind and are removed. This method does not guarantee complete purification of drinking water from fluoride. But it is cheap and possible in industrial production.
The electrolytic method is used as a pretreatment. It reduces the wear and tear of the filters and removes large impurities.
Shower water filter are a cheap way to purify drinking water. However, it will only be effective if replaced frequently. The most acceptable economy option for home filtration.
Water filters with reverse osmosis are more productive. A special membrane keeps out impurities and organics.
The fluoride removal industry uses a settling tank in which aluminum electrodes are immersed. Two purification methods are combined: electrolytic purification and precipitation with aluminum dioxide of fluorides. Additionally, copper, iron and other harmful substances are deposited on the electrodes.
Specialists recommend using shower water filter for your home. If it is necessary to filter all the water, a hybrid system with several degrees of purification is used. Separation of water streams is allowed: for drinking and for domestic needs. The external action of fluoride is not as destructive as the internal one.
Buy in our shop and read article about "Overview of Chlorine Shower Filter"